WHAT IS SILICA?
Silicon (Si) is naturally occurring and the second most common element in the Earth’s crust. The compound silica, also known as silicon dioxide (SiO2), is formed from silicon and oxygen atoms. Since oxygen and silicon make up about 75% of the Earth’s crust, the compound silica is very common. It is found in many rocks, such as granite, sandstone and slate as well as in sand and soil. The most common type of crystalline silica is quartz.
WHERE IS SILICA USED?
Silica is very commonly used in construction and at various concentrations in bricks, blocks, tiles, slabs, cement and concrete.
Silica dust is found in many products in our day- to-day lives such as glass, composite stone, ceramics, semi-conductors and much more.
WHAT IS SILICA DUST?
Silica dust is generated in workplace mechanical processes such as crushing, cutting, drilling, grinding, sawing or polishing of natural stone or man-made products that contain silica.
Some dust particles can be so small that they are not visible; these are commonly referred to as respirable particles. Respirable silica dust particles are small enough to penetrate deep into the lungs and can cause irreversible lung damage. The non-crystalline or amorphous forms of silica do not cause this kind of lung damage.
WHAT IS SILICOSIS?
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust, and is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs.Silicosis (particularly the acute form) is characterised by shortness of breath, cough, fever, and cyanosis (bluish skin).
There is no cure for silicosis, and it can be fatal.
CERAMIC TILES AND SILICA DUST
Unlike many other engineered products, ceramic tiles are made from a combination of clays, feldspars and other natural occurring minerals, mixed and ground in water and fired in a high temperature kiln. As a final inert product they only contain a fraction of sintered crystalline silica.
Tile products are odourless , stable, non-flammable , does not release any hazardous chemical and are considered as non- hazardous to health under normal conditions of use.
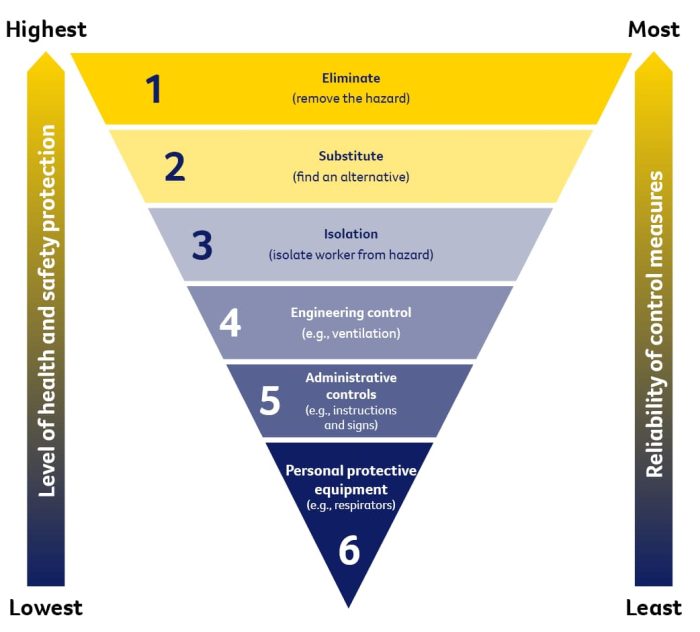
EFFECTIVE CONTROLS
Exposure to hazards can generally be reduced by following the Hierarchy of Control, risk management process below:
For additional information and resources, download the following documents:
SILICA SAFETY IN CONSTRUCTION – SAFETY CHECK LIST